

The most common ages are from 1 to 3 years old. The tubes help drain this fluid, and prevent it from building up. Sometimes, even after the infection is gone, some fluid may remain in the ear. During an ear infection, fluid gathers in the middle ear, which can affect your child’s hearing. The tubes are placed to help drain the fluid out of the middle ear in order to reduce the risk of ear infections. The tubes may be made of plastic, metal, or Teflon®. Myringotomy tubes are small tubes that are surgically placed into your child’s eardrum by an ear, nose, and throat surgeon. However, a small percentage of patients require a second procedure.(Also called ear tubes, tympanostomy tubes, or ventilation tubes) After surgery, drainage should stop and the hole in the eardrum should heal on its own.
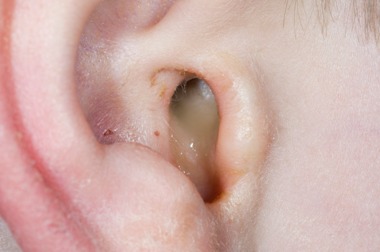
The surgeon may then insert a tube that will remain in place for a few months. During a myringotomy, an opening is made in the eardrum to drain excess fluid. It is performed to drain fluid from the ear, restore lost hearing, relieve pain and prevent infections. Myringotomy is the most frequently performed ear operation and the second-most common surgical procedure in children younger than two. The fluid in the ear canal is suctioned out, and a small tube is put in place to allow future drainage in the event of an infection. During a myringotomy, an incision is made into the ear drum, or tympanic membrane. Myringotomy with the insertion of ear tubes is an optional treatment for inflammation of the middle ear.
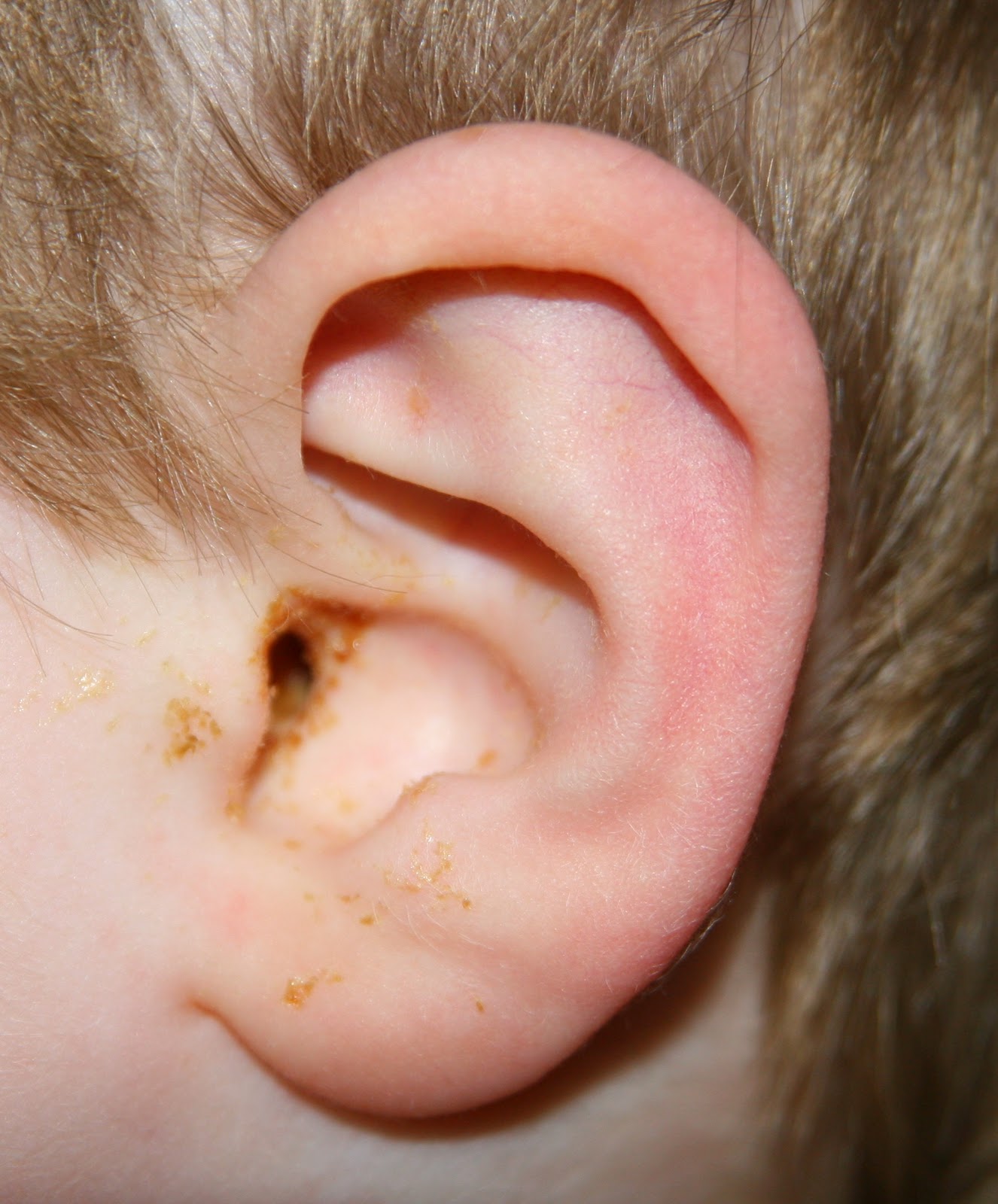
It involves the use of a graft (typically taken from the patient’s own tissues) to close the perforation and improve hearing. Tympanoplasty, a surgical procedure to repair a damaged or perforated eardrum, may be recommended for patients suffering from chronic ear infections or presenting symptoms of hearing loss. In many cases, the surgery provides considerable relief from symptoms and prevents further complications related to untreated ear conditions. It’s important to discuss these potential risks and benefits with your ENT provider when considering a mastoidectomy. In a mastoidectomy, the surgeon removes the diseased portion of the mastoid bone or the cholesteatoma, and this procedure can significantly improve the patient’s condition.Ĭomplications from surgery are rare but may include drainage from the ear, infection, temporary dizziness or loss of taste on one side of the tongue, hearing loss and, rarely, nerve injury to the side of the face operated upon.
TUBE EAR INFECTION PROFESSIONAL
When non-surgical interventions like antibiotics or professional ear cleaning fail to effectively address these conditions, a surgical procedure called a mastoidectomy may be recommended. Ear infections or disease in the ear or elsewhere can cause those spaces to fill with fluid, mucus or excess tissue (such as a cholesteatoma, a benign tumor that may grow out of a healing perforated ear drum and cause hearing damage). Located behind the ear, the mastoid bone connects to the middle ear and contains many air-filled spaces when healthy. However, when they become enlarged, they can cause health issues such as difficulty breathing, recurrent ear infections, or persistent sinusitis. These adenoids are soft tissues located at the back of the nose above the throat, playing a crucial role in the immune system particularly during early childhood. In addition, adenoids may themselves become infected, and the infection may spread into the eustachian tubes.Īn adenoidectomy, a surgical procedure to remove the adenoids, may be recommended for patients with enlarged adenoids (see “ symptoms of enlarged adenoids“), those forced to breath through mouth, or snoring. Enlarged adenoids can, because of their size, interfere with the eustachian tube opening. They are positioned in the back of the upper part of the throat near the eustachian tubes. Adenoids are composed largely of cells (lymphocytes) that help fight infections.
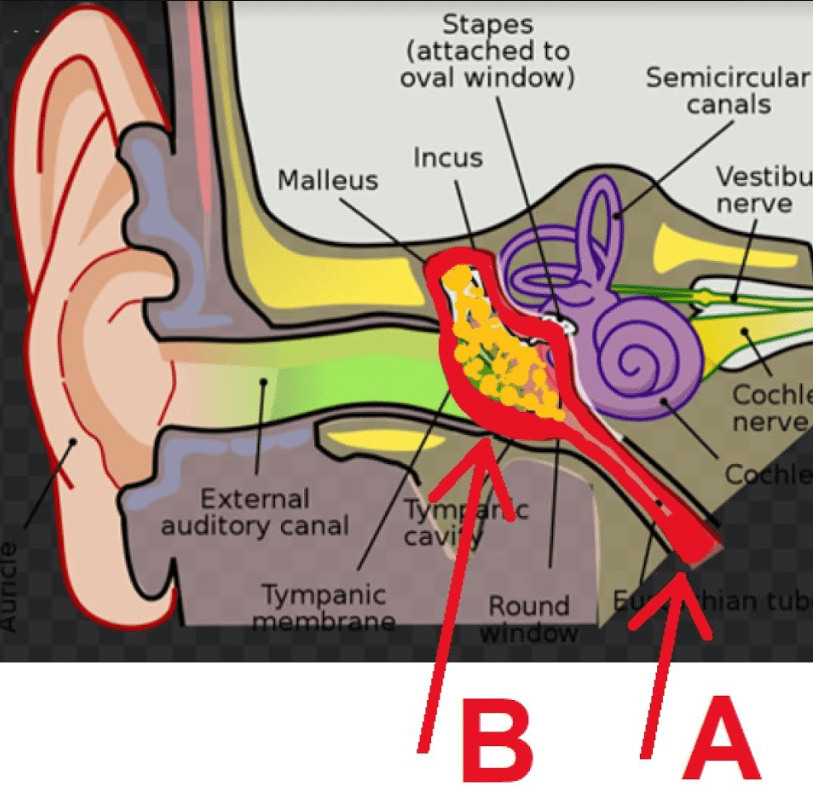
One factor that makes children more susceptible to otitis media is that adenoids in children are larger than they are in adults (see enlarged adenoids). Almost half of these children will have three or more ear infections during their first 3 years.Seventy-five percent of children experience at least one episode of otitis media by their third birthday.These can be viral or bacterial infections.Īlthough otitis media is primarily a disease of infants and young children, it can also affect adults. This inflammation often begins with infections that cause sore throats, colds, or other respiratory or breathing problems spread to the middle ear. Otitis media (ear infection) is an infection or inflammation of the middle ear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
